What is Cloud Security?
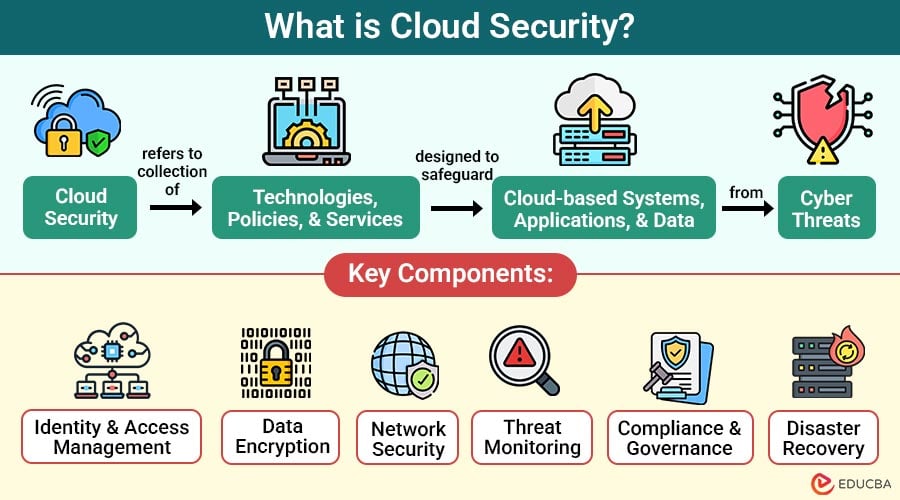
Cloud security refers to a collection of technologies, policies, and services designed to safeguard cloud-based systems, applications, and data from cyber threats. It encompasses measures such as encryption, access control, identity management, intrusion detection, and regulatory compliance to ensure that cloud resources remain safe from unauthorized access, data loss, or service disruptions.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud security safeguards digital trust by proactively preventing cyber risks across dynamic, distributed IT environments.
- Effective cloud defense blends people, processes, and technology into a resilient security operations framework.
- Protecting workloads in the cloud requires continuous visibility, policy enforcement, and data lifecycle control.
- Modern threats demand adaptive cloud security measures that evolve with changing architectures and compliance needs.
Why Cloud Security Matters?
As more organizations embrace cloud solutions, they face new and evolving cyber threats. Here is why cloud security is crucial:
1. Data Protection
Cloud systems store sensitive data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals and increasing the risk of data breaches.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Financial and healthcare sectors are subject to stringent rules, including GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
3. Business Continuity
Security incidents can severely disrupt operations, harm a company’s reputation, and result in significant financial and legal consequences.
4. Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud security is a joint effort; user-side misconfigurations or negligence can introduce serious security gaps and vulnerabilities.
Key Components of Cloud Security
To build a secure cloud infrastructure, you must understand the key pillars of cloud security:
1. Identity and Access Management
IAM aids in limiting access to cloud resources to authorized users only. Among the methods are least privilege access, single sign-on (SSO), and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
2. Data Encryption
Data must be encrypted both at rest and in transit to protect against unauthorized access. Cloud providers offer built-in encryption features, but businesses should implement end-to-end encryption for sensitive data.
3. Network Security
Protecting cloud networks from malicious assaults requires the use of firewalls, secure virtual private networks (VPNs), and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS).
4. Threat Monitoring
Continuous monitoring tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) detect anomalies and respond to threats in real time.
5. Compliance and Governance
Cloud security frameworks help organizations comply with laws and regulations. Popular standards include ISO 27001, SOC 2, and NIST.
6. Disaster Recovery
Plans for backup and disaster recovery reduce downtime and data loss by guaranteeing data availability during outages or cyberattacks.
Common Cloud Security Threats
Here are the most prevalent threats that organizations face when securing their cloud environments:
1. Data Breaches
Unauthorized access due to poor controls or misconfigurations can expose sensitive data, leading to severe reputational and financial consequences.
2. Misconfigured Cloud Settings
Open storage, unrestricted ports, or incorrect permissions can expose cloud resources, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access and data leaks.
3. Insider Threats
Employees with legitimate access may intentionally or accidentally leak sensitive data, damage systems, or compromise compliance, causing major organizational risks.
4. Account Hijacking
Phishing or credential attacks can compromise cloud accounts, enabling attackers to manipulate data, change settings, or deploy malicious applications unnoticed.
5. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Overwhelming traffic floods from attackers can crash cloud services, degrade performance, disrupt availability, and impact user access to critical applications.
Best Practices
Implementing strong cloud security involves a proactive and layered approach. Here are the essential best practices:
1. Adopt a Zero Trust Architecture
Always verify users and devices continuously; never assume trust without strict authentication and authorization checks.
2. Implement Strong IAM Policies
Use RBAC, MFA, and review user permissions regularly to ensure minimal, appropriate access to cloud resources.
3. Automate Security Operations
Deploy automation for patching, threat detection, and compliance to reduce manual effort and prevent human-induced errors.
4. Regular Security Assessments
Conduct vulnerability scans and penetration tests frequently to uncover and resolve security gaps before attackers exploit them.
5. Secure APIs
Protect APIs using secure coding, restrict access exposure, enforce authentication, and monitor traffic for suspicious activity.
6. Employee Training
Educate staff regularly on cybersecurity awareness, phishing scams, and proper cloud practices to reduce internal security risks.
Cloud Security in Different Cloud Models
Security requirements and responsibilities vary depending on the cloud deployment model. Here is how security is approached in each model:
1. Public Cloud
Third-party companies such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud own and run public clouds. Security responsibilities are shared, but users must ensure proper configurations and data encryption.
2. Private Cloud
Private clouds, when used by a single business, provide more protection and control. However, the organization bears full responsibility for security measures.
3. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud
Hybrid clouds combine on-premise and cloud environments, while multi-cloud uses services from multiple providers. Ensuring consistent security policies across platforms is crucial.
Tools and Technologies in Cloud Security
Here are the key tools and technologies that help safeguard cloud environments against threats, misconfigurations, and data breaches.
1. Cloud Access Security Broker
Acts as an intermediary enforcing security policies between cloud users and providers, offering visibility, control, and data protection.
2. Cloud Security Posture Management
Continuously monitors cloud environments to detect misconfigurations, enforce compliance standards, and improve overall cloud infrastructure security posture.
3. Cloud Workload Protection Platforms
Provides security for applications and workloads across cloud environments, detecting threats and vulnerabilities in real time during operations.
4. Encryption Key Management
Securely manages, rotates, and stores encryption keys to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with encryption policies and regulations.
Future Trends
Here are the emerging trends shaping the future, driven by innovation, automation, and evolving threat landscapes:
1. AI and ML Integration
AI-driven tools will proactively detect threats, automate incident responses, and predict attacks by analyzing large volumes of security data.
2. Secure Access Service Edge
SASE protects distant users and apps in dispersed environments by combining networking and security features into a cloud-delivered service.
3. Confidential Computing
Encrypts data during processing within a secure enclave, ensuring sensitive information remains protected even while in active use or execution.
4. Compliance Automation
Automated systems streamline compliance tasks, conduct continuous audits, and ensure organizations meet evolving regulatory and industry-specific security requirements efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who is responsible for cloud security?
Answer: Both the cloud provider and the user share responsibility. Providers secure the infrastructure, while users must manage data, identity, and access.
Q2. Is cloud security better than traditional security?
Answer: Cloud security can be more robust due to built-in tools, automated monitoring, and scalability. However, it depends on proper implementation and governance.
Q3: How can I ensure compliance in the cloud?
Answer: Use compliance tools, follow regulatory frameworks, perform regular audits, and keep documentation for proof of compliance.
Q4. What industries need cloud security the most?
Answer: Healthcare, finance, government, education, and e-commerce—basically, any sector handling sensitive data.
Final Thoughts
Cloud security must continue to be a primary concern as cloud adoption grows. It is not just about defending data—it is about ensuring trust, compliance, and business resilience. A proactive strategy, combined with the right tools and policies, empowers organizations to thrive securely in the digital age.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cloud Security” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
- Cloud Security Services
- Cloud Security Tools
- Cloud Computing Security Architecture
- Cloud Access Security Brokers

